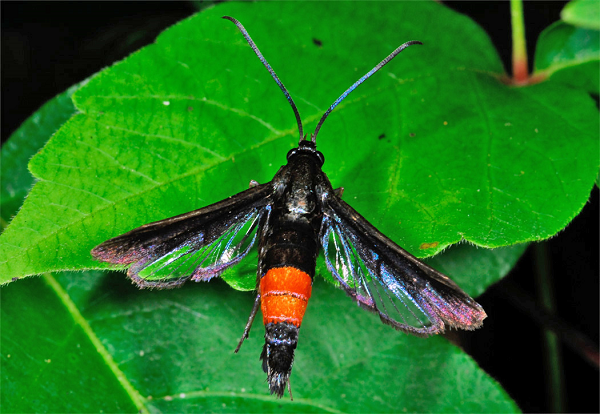
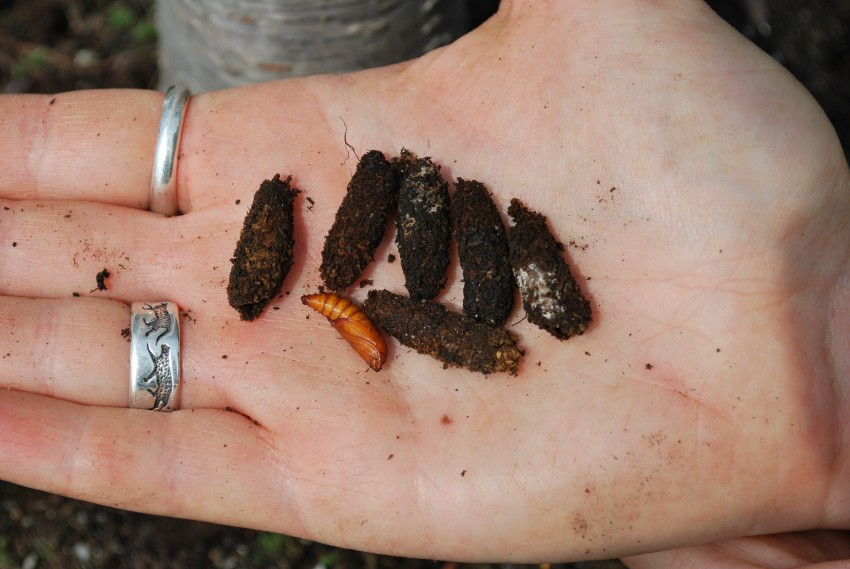
peach tree borer life cycle
When mature the larva constructs a cocoon under the bark at or near soil level and pupates. Abundant peach tree borers seriously weaken and even kill trees.

Peachtree Borer Nc State Extension Publications
Much of the United States including Texas and Nebraska has one generation per year.
. Life Cycle The period of time required to complete a life cycle varies considerably throughout the range of the peachtree borer. In the spring feeding is resumed and the larval period is completed. Upon hatching the larvae bore just beneath the bark near the ground level and into the roots to feed on growing tissue and inner bark.
Adult moths of the lesser peachtree borer emerge from late May through September while peachtree borers emerge from midJune to early September. Life Cycle Appearance Female Peachtree Borers lay their eggs on the tree trunks or at the base of the tree and lay 500-600 eggs on average. The peach tree borer completes one life cycle a year.
The adult borer emerges in the late spring and early summer. Adult beetles usually appear in May and June with egg-laying continuing until late July. As temperatures warm up they resume boring and usually complete their feeding in May.
In the spring feeding is resumed and the larval period is completed. The period of time required to complete a life cycle varies considerably throughout the range of the peachtree borer. Life Cycle The period of time required to complete a life cycle varies considerably throughout the range of the peachtree borer.
The immature larva stage Figure 2 produces tree damage. Larvae become active and resume feeding in April with larger larvae. The clear-winged female moths lay their eggs on the bark at the base of tree trunks in mid- to late-summer.
Adults begin emerging in late spring and early summer from larvae that have overwintered inside the tree an inch or two beneath the soil line. Because the egg laying period is so long overwintering larvae vary greatly in size. Larvae immediately enter the bark usually through wounds and begin feeding and growing.
Egg laying begins soon after emergence and mating and larvae tunnel into the bark to feed until the. The entire life cycle of the peach tree borer requires one year to complete. Expect your peach tree to produce fruit for about 12 years.
They continue to emerge throughout the. It is reported that it takes two years to complete a life cycle in Canada and in a small percentage of populations in New York. Peach tree borers attack near the soil line with most activity occurring a few inches 5 to 75 cm below the ground.
Much of the United States including Texas and Nebraska has one generation per year. Peach Tree Borers feed under the bark of Peach trees and are a serious pest in commercial peach orchards. Adults which resemble wasps are most prevalent from mid-May to early October.
Usually they are close to or below ground level. Eggs hatch in 8 to 30 days and the larvae attempt to bore into the bark. It is reported that it takes two years to complete a life cycle in Canada and in a small percentage of populations in New York.
The lesser borer completes about one and one-half cycles a year. In most areas of the state it is necessary to periodically control this insect to maintain tree vigor. Because the egg laying period is so long overwintering larvae vary greatly in size.
In the spring feeding is resumed and the larval period is completed. Peachtree borer has a single generation per year but it can result in severe losses if not managed correctly. The peachtree borer overwinters as a partly grown larva in its burrow beneath the bark of the tree.
Usually they are close to or below ground level. During this time eggs are laid on. The lesser peachtree borer overwinters as larvae and reaches full growth during April and May.
The life cycle of the peachtree borer requires one year to complete. Upon hatching from the eggs young larvae. Eventually the bark begins to peel off damaged areas making the tree susceptible to other pests and disease.
This borer overwinters in a wide range of larval stages. To survive they must get under dead bark near live bark where they have protection for feeding. Only the immature larva stage Figure 3 produces the damage to trees.
The adults are clear-winged day-flying moths which are often mistaken. Winter is spent as a larva under the bark in the cambium layer. The pests life cycle and treatment is similar to those of exitiosa.
Life Cycle and Damage Peach tree borers overwinter as partially grown larvae in a gallery under the bark. The first flight occurs during May and June and the second during August and September. The adult peachtree borer is a steel blue to black moth that resembles a wasp.
Much of the United States including Texas and Nebraska has one generation per year. As temperatures warm up they resume boring and usually complete their feeding in May. Damage Any wound on stone fruit trees may cause gum to exude.
The borer has a two-year life cycle. There is one generation of PTB a year. Unlike most moths PTB are active during the day mostly between late morning and early afternoon Mated females deposit anywhere from 200 to 800 eggs near the bases of trees with eggs hatching in 9 to 10 days.
Life Cycle and Damage Peach tree borersoverwinter as partially grown larvae in a gallery under the bark. They also attack Plums and Cherry trees in the residential landscape and can weaken and eventually kill these trees by girdling the trunks under the bark. Life Cycle The peachtree borer overwinters as a partly grown larva in its burrow beneath the bark of the tree.
Life cycles of peachtree borers and lesser peachtree borers. It is reported that it takes two years to complete a life cycle in Canada and in a small percentage of populations in New York. There are two and possibly a partial third generations each year.
Do peach trees produce fruit every year. The tree should start bearing large crops by the third or fourth year after planting and reach peak production from eight years until it begins its decline around year 12. Larvae eat an exit hole nearly through the bark spin a cocoon and pupate in a small cavity.
Eggs typically are inserted into the bark of the trunk near the ground although eggs may occasionally be laid in tree crotches. Hatching larvae tunnel into the tree at or slightly below ground level. Peach trees do not produce fruit every year.

Lesser Peachtree Borer Damage Stock Image C025 7085 Science Photo Library

Peachtree Borer Nc State Extension Publications
Pests Bc Tree Fruit Production Guide

Peach Tree Borer Treatment Control Planet Natural
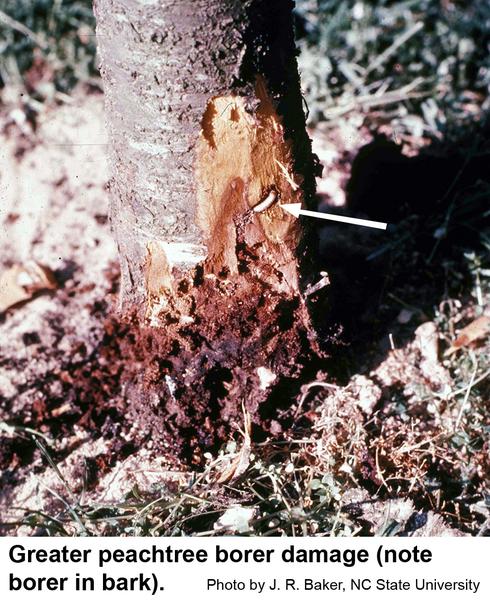

Greater Peachtree Borer In The Landscape Nc State Extension Publications

Peach Tree Borers How To Control Peach Tree Borers
Pests Bc Tree Fruit Production Guide

Peachtree Borer 5 566 Extension
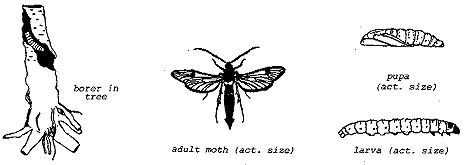
Lords Environmental Peach Tree Borers
Peachtree Borer Wsu Tree Fruit Washington State University
Eny 691 In489 Peachtree Borers In The Home And Commercial Peach Orchard

Goes To Show You Don T Ever Know Plant Pest Advisory

Peach Tree Borer Fairfax Gardening


